Unknown Environment
Drone Path Planning
Global planner implementation using Dijkstra algorithm for a quadrotor in PyBullet simulation, ensuring safe maneuverability and collision avoidance.
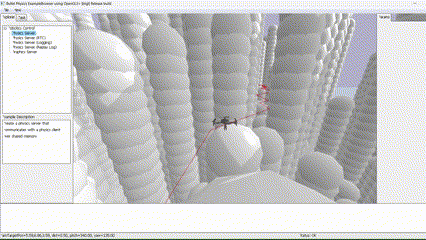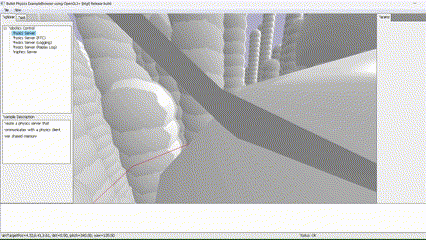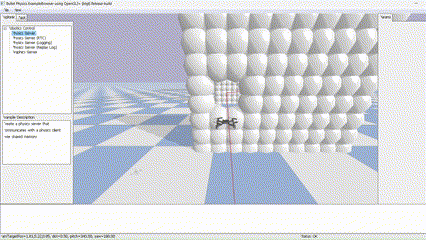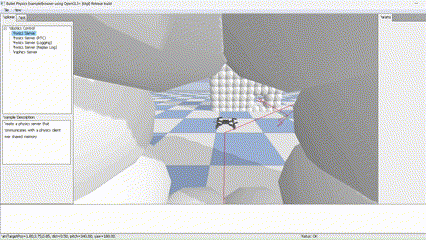
Global planner implementation using Dijkstra algorithm for a quadrotor in PyBullet simulation, ensuring safe maneuverability and collision avoidance.

This project was developed for the "Planning and Decision Making" course in the Robotics Master at TU Delft. The primary objective was to engineer a robust global planner capable of guiding a quadrotor safely through diverse, obstacle-ridden environments within a physics-based simulation.
The core challenge involved implementing the Dijkstra algorithm from scratch and integrating it seamlessly into the PyBullet simulation environment to enable autonomous navigation in 3D space.
The foundation of the planner is a voxel-based grid system. The simulation space is discretized into nodes, where each node is validated against the environment boundaries and obstacle positions. This creates a navigable graph for the pathfinding algorithm.
def filter_grid(XYZ):
indices_to_remove = []
for i, point in enumerate(XYZ):
# Check bounds
if (X_BOUNDS[0] <= point[0] <= X_BOUNDS[1]) and \
(Y_BOUNDS[0] <= point[1] <= Y_BOUNDS[1]) and \
(Z_BOUNDS[0] <= point[2] <= Z_BOUNDS[1]):
# Check collision
if not euclideanDistance(point):
indices_to_remove.append(i)
else:
indices_to_remove.append(i)
return np.delete(XYZ, indices_to_remove, axis=0)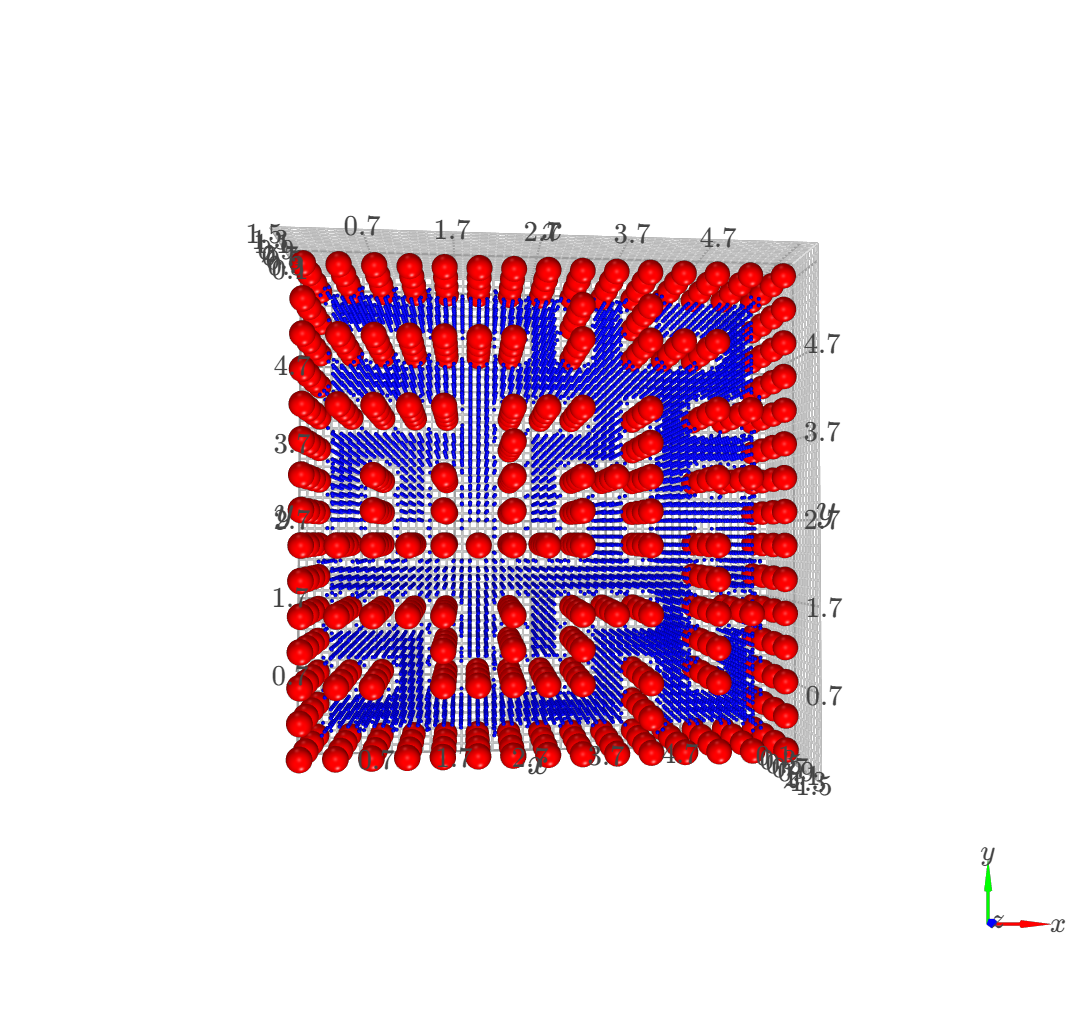
High Resolution Grid (0.1 spacing)
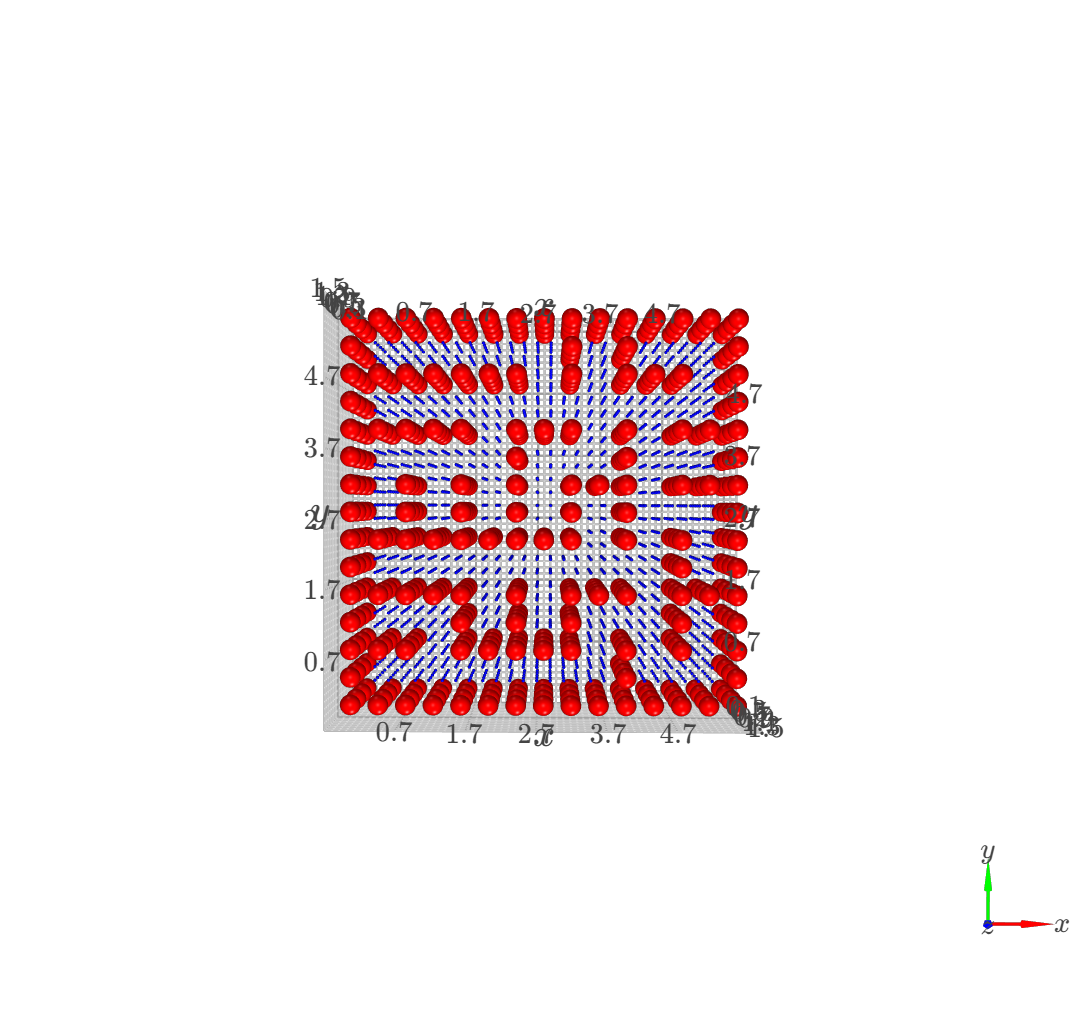
Low Resolution Grid (0.2 spacing)
Institution Technical University of Delft (TU Delft)
Course Planning and Decision Making
Team Guillem Ribes